

By Rachel Karambelas, marketing communications specialist, Phoseon Technology
Adhesive bonding, sealing, as well as coating processes in factory assembly lines are rapidly upgrading to UV LED curing technology because of all the advantages. UV LED technology offers lower operating costs, longer lifetime, enhanced system capabilities and environmental benefits compared to traditional mercury UV curing.
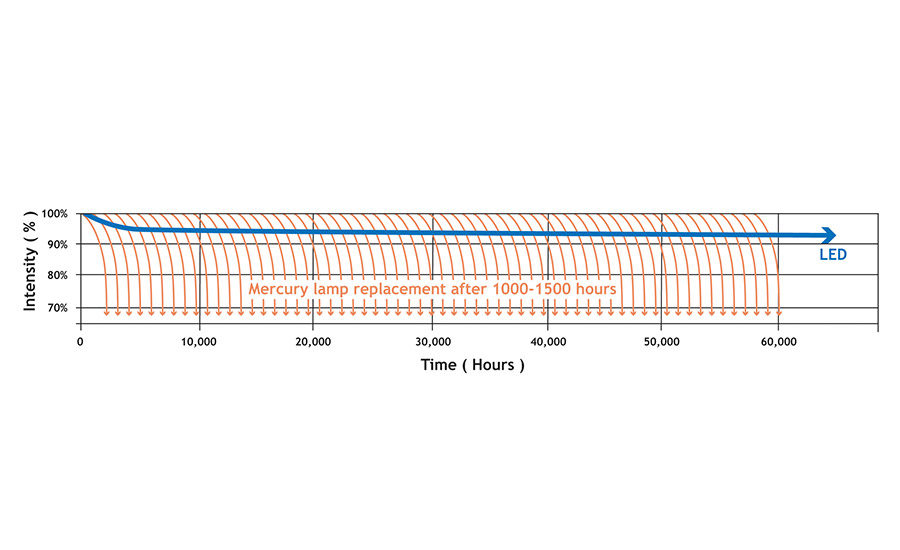
Traditional mercury UV bulbs degrade over time, making them unstable and in need of replacement every 1,000 - 1,500 hours. In contrast, UV LED provides stable UV output consistently over many years, leading to better process control and stability for manufacturing operations. UV LED curing technology offers lower operating costs, long lifetime, enhanced system capabilities due to being a solid state device, and environmental benefits associated with safer workplace environments. In addition, UV LED provides a low temperature light source for small components that may be sensitive to heat.
UV LED curing offers multiple advantages:
Depth of cure - with long wavelengths in the UVA range, UV LEDs offer excellent depth of cure. Because of these long wavelengths, UV LEDs are significantly more effective at curing adhesives than mercury lamps. The higher irradiance of UV LEDs at 365Nm penetrates deep into the chemistry, making the technology ideally suited for adhesive and sealant applications. Adhesive chemistries include silicones, acrylate/urethanes, cyanoacrylates, anaerobics, pressure sensitive adhesives, film adhesives, and epoxies.
Full cure - the stable and long lived output of the LED lamp ensures full cure all the time. UV LED lamps have been reported to exceed 60,000 hours while still producing the specified power.
Low heat - UV LEDs do not generate any infrared output that is translated into heat. This is extremely important on manufacturing lines where the introduction of heat results in changes in the chemical properties of the adhesive or deformation of the substrate. In some cases, heat can lead to material warping, lack of adhesion and eventually scrap. UV LEDs are a ‘cool’ light source; the only heat generated is a byproduct of the absorption of UV energy.
No replaceable components - conventional mercury bulbs have a short lifetime, while LED curing lamps can extend beyond 60,000 hours if maintained properly. Upgrading to UV LED eliminates replacement costs associated with traditional UV technology.
Reliability - LED technology is a solid state technology that does not degrade, even when continuously flashed on and off. The long lifetime, instant on/off control, and consistent UV output reduces process variability and advances process control. With thousands of commercial installations across the world, LED curing technology has been proven to be extremely reliable.
Applications
UV adhesive curing application segments include electronic assembly, automotive, medical, ammunitions, pressure sensitive films, general assembly, and other manufacturing processes.
UV LED curing technology is ideally suited for electronic assembly applications. The combination of high energy UV LED sources with the appropriate adhesive enables increased productivity while also providing the ability to cure heat sensitive materials. Today, many electronics manufacturers use UV LED curing in the production of products such as touchscreens, mobile phones, micro-speakers, and hard disk drives.
This video showcases the use of UV LED to cure adhesives during micro-speaker assembly applications:
In automotive coating applications, UV LED provides near instant curing of functional and decorative coatings. The lightweight materials used in today’s automobiles benefit from the low temperature of UV LED technology. The automotive industry uses UV LED curing solutions for forward lighting, tail lenses, interior and exterior trim components, and body panels.
Adhesives used in medical applications, such as syringes, catheters, IV delivery systems, endoscopes, and hearing aids, often benefit from UV curing technology. Properties such as better uniformity, low heat, instant on/off, and long lifetime are ideal for this highly regulated industry.
UV LED curing solutions are used in ammunition production for waterproofing, adhesive bonding, sealing, and coating. The UV LED curing of external ammunition sealants can make bullet pull strength more consistent, thereby improving performance and accuracy. Example ammunitions related applications include external ammunition sealing (i.e waterproofing); igniter, fuse, and detonator UV sealing; speciality UV coatings and primers; blank ammunition sealing; shot shell crimp sealing; and tip colour coding.
General assembly, industrial grade bonding processes require products that can work in tough, sometimes harsh manufacturing environments. Industrial UV LED curing applications include EV batteries, solar panels, wood/plastic coatings, thin films, bottle processing, aviation, automobiles, and many others. 
Improving manufacturing processes
UV LED curing offers manufacturers higher yield rates and productivity due to a consistent and stable process with less damage to heat-sensitive components. In addition, UV LEDs are highly efficient, offering significant energy cost savings. They require very little space, making them easy to integrate into small spaces. Since UV LEDs produce no ozone emissions or hazardous waste concerns, they are an environmentally friendly and safe UV curing technology.
Adhesive and coating suppliers have formulations available for use with UV LED curing that are easy to handle and apply in the precision, high-speed processes that are so common in manufacturing. When looking to improve yield rates through higher productivity and reduced scrap, manufacturers should consider UV LED curing technology.
Environmentally sustainable technology
LED is the only sustainable choice for UV curing. LED technology does not contain toxic mercury like traditional UV curing technology. The regulation of mercury in manufacturing processes is growing globally.
For example, the Minamata Convention on Mercury is a global treaty to protect human health and the environment from the adverse effects of mercury. Highlights of the convention include a ban on new mercury mines, the phase out of existing mines, the phase-out and phase down of mercury use in several products and processes, control measures on emissions to air and on releases to land and water, and the regulation of the informal sector of artisanal and small-scale gold mining. The convention also addresses interim storage of mercury and its disposal once it becomes waste, sites contaminated by mercury, and health issues.
Traditional UV-curing mercury bulbs also produce harmful gases and ozone that must be evacuated from the work area (and often completely out of the facility). The required exhaust systems are bulky, loud, and require a significant amount of energy. UV LED does not generate greenhouse gases or ozone, and it reduces CO2 emissions by more than 50% compared to mercury lamps.
As a result of the need for numerous bulb replacements, conventional mercury lamps generate a significant amount of waste over time. The long lifetime of properly maintained LED curing lamps results in less waste, as well as the elimination of the associated replacement costs.
Traditional mercury UV lamps require a significant amount of electricity to operate. By upgrading to UV LED, users have experienced energy savings of up to 85%. A key contributing factor to this savings is the instant on/off nature of the technology. LED lamps are only on when they are curing; in standby mode, they are completely off.
Worldwide solutions
UV LED solutions are being used worldwide for curing adhesives, sealants, and coatings. Recognised advantages include lower operating costs, enhanced system capabilities, and environmental benefits that contribute to a safer and more productive workplace.

Having spent a decade in the fastener industry experiencing every facet – from steel mills, fastener manufacturers, wholesalers, distributors, as well as machinery builders and plating + coating companies, Claire has developed an in-depth knowledge of all things fasteners.
Alongside visiting numerous companies, exhibitions and conferences around the world, Claire has also interviewed high profile figures – focusing on key topics impacting the sector and making sure readers stay up to date with the latest developments within the industry.





